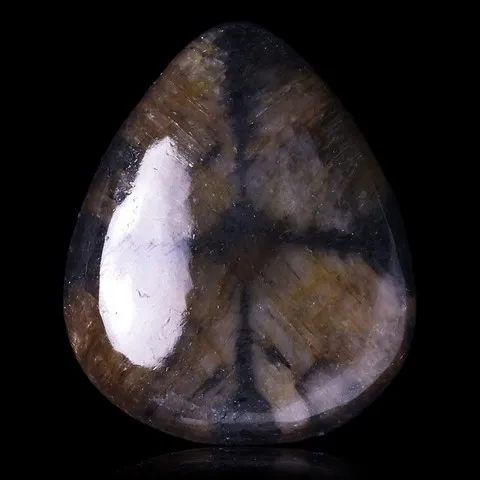
ANDALUSITE
Class : Silicates
Subclass : Nesosilicates
Crystal System : Orthorhombic
Chemistry : Al2SiO5
Rarity : Very common
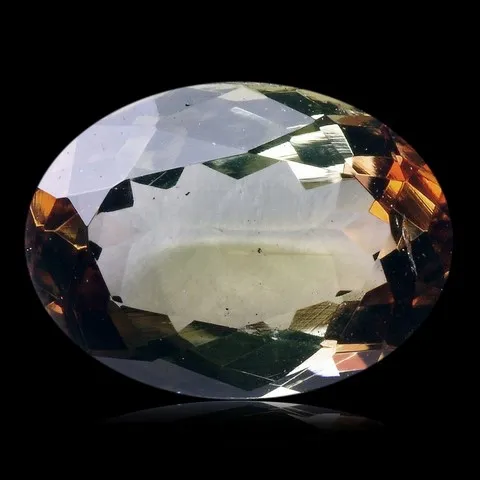
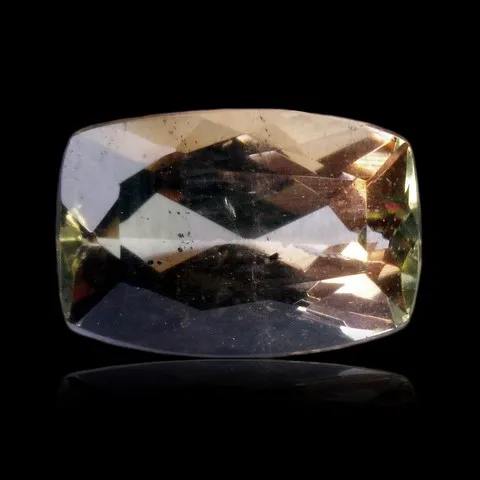
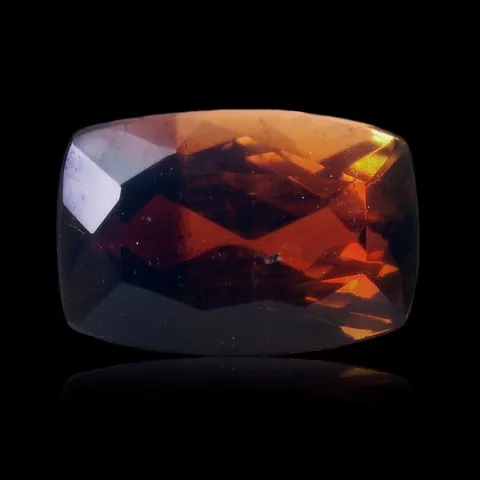
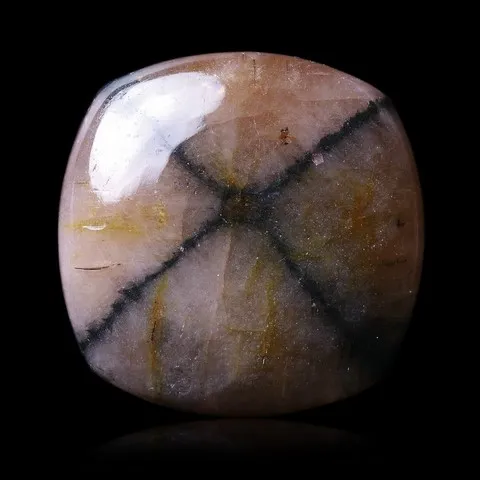
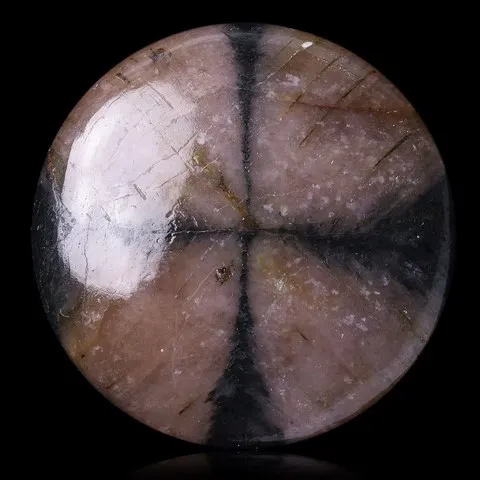
Andalusite is the polymorph of kyanite and sillimanite. It is a common mineral, typical of aluminous rocks affected by regional metamorphism of low pressure or by contact metamorphism (cordierite-andalusite schists, hornfels, etc...) more rare in very aluminous granites and leucogranites and their pegmatites. It owes its name to its region of discovery : Andalusia, in Spain. It is presented in very coarse prisms with square sections, up to 20 cm long. Sometimes massive or with a radiated texture, most often stony and altered superficially in sericite, andalusite has a vitreous luster and is white to pink in color, sometimes greenish to purple or red. It can present a strong purple-green to green dichroism. Chiastolite is a variety with charcoal inclusions arranged in a cross pattern (main photo). Andalusite is the raw material and "ore" of mullite, the mineral at the base of the refractory products industry, in particular bricks, ceramics and porcelains resistant to high temperatures. The gemmy and strongly dichroic (green-red) varieties from California and Brazil are frequently cut as gemstones and used in jewelry.
Andalusite in the World
Andalusite in France
Fakes and treatments
Hardness : 6.5 to 7.5
Density : 3.13 to 3.21
Fracture : Uneven to sub-conchoidal
Streak : White
TP : Translucent to transparent
IR : 1.629 to 1.650
Birefringence : 0.009 to 0.010
Optical character : Biaxial -
Pleochroism : Green to red
Fluorescence : Green to yellow
Solubility : Hydrofluoric acid
Magnetism : None
Radioactivity : None